|
从服务器端的打印结果可以看出,IE浏览器发送的HTTP请求采用GET方式,请求的URI为login.htm。服务器把login.htm文件发送给IE浏览器,IE浏览器将它呈现给用户。login.htm文件中的内容如下:
<html>
<head>
<title>helloapp</title>
</head>
<body >
<form name="loginForm" method="post" action="hello.htm">
<table>
<tr><td><div align="right">用户名:</div></td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"></td>
</tr>
<tr><td><div align="right">口令:</div></td>
<td><input type="password" name="password"></td>
</tr>
<tr><td></td>
<td><input type="submit" name="submit" value="submit"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
在login.htm文件中定义了一个HTML表单,它有两个输入框,分别用于输入用户名和口令。以上<form>元素的action属性指定当用户提交表单时所请求访问的网页,此处为hello.htm;method属性用于指定请求方式,此处为POST。
在图2的网页中,输入用户名“weiqin”,口令“1234”,然后提交表单。图3显示了IE浏览器接收到的网页,以及服务器接收到的HTTP请求。
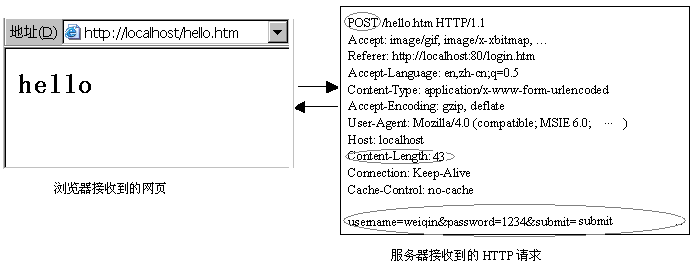
图3 浏览器按照POST方式访问hello.htm
从图3可以看出,当提交了表单,浏览器将采用POST方式请求访问hello.htm。表单中输入的用户名和口令等数据位于HTTP请求的正文部分,正文与请求头之间以空行分割。请求头中的Content-Length项指定正文的长度,此处为43个字符。本例中的SimpleHttpServer并没有对请求正文作任何处理。在实际应用中,HTTP服务器应该具备解析请求正文,生成动态网页的能力。
(3)把login.htm文件中method属性的值改为“GET”:
<form name="loginForm" method="get" action="hello.htm">
再重复上述步骤,当再次提交表单时,浏览器将采用GET方式请求访问hello.htm。服务器端接收到的HTTP请求如下:
GET /hello.htm?username=weiqin&password=1234&submit=submit HTTP/1.1
Accept: image/gif, image/x-xbitmap, image/jpeg, image/pjpeg, application/x-shock
wave-flash, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint, application/vnd.ms-excel, application
/msword, */*
Referer: http://localhost/login.htm
Accept-Language: en,zh-cn;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.0)
Host: localhost
Connection: Keep-Alive
//此处为一空行
在GET方式下,表单中的数据将不再作为请求正文发送,而是直接放在HTTP请求的第一行的URI里面,文件名与表单数据之间以“?”分割。
在以上HTTP请求中,username和password也被称为请求参数,它们都有相应的参数值,比如username参数的值为weiqin,password参数的值为1234。服务器可以读取这些请求参数的值,然后作相应处理。在GET方式下,请求参数位于HTTP请求的第一行的URI中,而在POST方式下,请求参数位于HTTP请求的正文中。
HTTP服务器的主要任务就是接收HTTP请求,然后发送HTTP响应。图4是本文所介绍的非阻塞的HTTP服务器的对象模型。
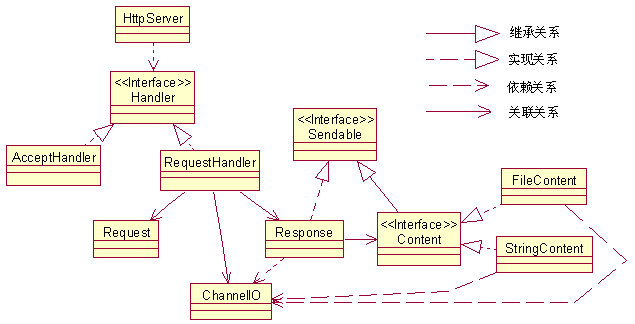
图4 HTTP服务器的对象模型
在这个对象模型中,HttpServer类是服务器主程序,由它启动服务器。AcceptHandler负责接收客户连接,RequestHandler负责接收客户的HTTP请求,对其解析,然后生成相应的HTTP响应,再把它发送给客户。Request类表示HTTP请求,Response类表示HTTP响应,Content类表示HTTP响应的正文。
1.服务器主程序:HttpServer类
HttpServer类是服务器的主程序,它仅启用了单个主线程,采用非阻塞模式来接收客户连结,以及收发数据。例程2是HttpServer类的源程序:
//例程2 HttpServer.java
//此处省略import语句
public class HttpServer{
private Selector selector = null;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
private int port = 80;
private Charset charset=Charset.forName("GBK");
public HttpServer()throws IOException{
//创建Selector和ServerSocketChannel
//把ServerSocketChannel设置为非阻塞模式,绑定到80端口
…
}
public void service() throws IOException{
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT,
//注册接收连结就绪事件
new AcceptHandler());
for(;;){
int n = selector.select();
if(n==0)continue;
Set readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = readyKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key=null;
try{
key = (SelectionKey) it.next();
it.remove();
final Handler handler = (Handler)key.attachment();
handler.handle(key); //由Handler处理相关事件
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
try{
if(key!=null){
key.cancel();
key.channel().close();
}
}catch(Exception ex){e.printStackTrace();}
}
}//#while
}//#while
}
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
final HttpServer server = new HttpServer();
server.service();
}
}
在HttpServer类的service()方法中,当ServerSocketChannel向Selector注册接收连接就绪事件时,设置了一个AcceptHandler附件:
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT,new AcceptHandler());
AcceptHandler类的handle()方法负责处理接收连结就绪事件。当某种事件发生时,HttpServer类的service()方法从SelectionKey中获得Handler附件,然后调用它的handle()方法:
final Handler handler = (Handler)key.attachment();
handler.handle(key); //处理相关事件
2.具有自动增长的缓冲区的ChannelIO类
ChannelIO对SocketChannel进行了包装,增加了自动增长缓冲区容量的功能。当调用socketChannel.read(ByteBuffer buffer)方法时,如果buffer已满(即position=limit),那么即使通道中还有未接收的数据,read方法也不会读取任何数据,而是直接返回0,表示读到了零个字节。
为了能读取通道中的所有数据,必须保证缓冲区的容量足够大。在ChannelIO类中,有一个requestBuffer变量,它用来存放客户的HTTP请求数据,当requestBuffer剩余容量已经不足5%,并且还有HTTP请求数据未接收,ChannelIO会自动扩充requestBuffer的容量,该功能由resizeRequestBuffer()方法完成。
例程3是ChannelIO类的源程序,它的read()和write()方法利用SocketChannel来接收和发送数据,并且它还提供了实用方法transferTo(),该方法能把文件中的数据发送到SocketChannel中。
//例程3 ChannelIO.java
//此处省略import语句
public class ChannelIO {
protected SocketChannel socketChannel;
protected ByteBuffer requestBuffer; //存放请求数据
private static int requestBufferSize = 4096;
public ChannelIO(SocketChannel socketChannel, boolean blocking)
throws IOException {
this.socketChannel = socketChannel;
socketChannel.configureBlocking(blocking); //设置模式
requestBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(requestBufferSize);
}
public SocketChannel getSocketChannel() {
return socketChannel;
}
/*
* 如果原缓冲区的剩余容量不够,就创建一个新的缓冲区,容量为原来的两倍,
* 把原来缓冲区的数据拷贝到新缓冲区
*/
protected void resizeRequestBuffer(int remaining) {
if (requestBuffer.remaining() < remaining) {
// 把容量增大到原来的两倍
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(requestBuffer.capacity() * 2);
requestBuffer.flip();
bb.put(requestBuffer); //把原来缓冲区中的数据拷贝到新的缓冲区
requestBuffer = bb;
}
}
/*
* 接收数据,把它们存放到requestBuffer中,如果requsetBuffer的剩余容量不足5%,
* 就通过resizeRequestBuffer()方法扩充容量
*/
public int read() throws IOException {
resizeRequestBuffer(requestBufferSize/20);
return socketChannel.read(requestBuffer);
}
/* 返回requestBuffer,它存放了请求数据 */
public ByteBuffer getReadBuf() {
return requestBuffer;
}
/* 发送参数指定的ByteBuffer中的数据 */
public int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException {
return socketChannel.write(src);
}
/* 把FileChannel中的数据写到SocketChannel中 */
public long transferTo(FileChannel fc, long pos, long len) throws IOException {
return fc.transferTo(pos, len, socketChannel);
}
/* 关闭SocketChannel */
public void close() throws IOException {
socketChannel.close();
}
}
3.负责处理各种事件的Handler接口
Handler接口负责处理各种事件,它的定义如下:
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
public interface Handler {
public void handle(SelectionKey key) throws IOException;
}
Handler接口有两个实现类:AcceptHandler和RequestHandler。AcceptHandler负责处理接收连结就绪事件,RequestHandler负责处理读就绪和写就绪事件。更确切地说,RequestHandler负责接收客户的HTTP请求,以及发送HTTP响应。
4.AcceptHandler类
AcceptHandler负责处理接收连结就绪事件。它获得与客户连接的SocketChannel,然后向Selector注册读就绪事件,并且创建了一个RequestHandler,把它作为SelectionKey的附件。当读就绪事件发生,将由这个RequestHandler来处理该事件。例程4是AcceptHandler类的源程序:
//例程4 AcceptHandler.java
//此处省略import语句
public class AcceptHandler implements Handler {
public void handle(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=(ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
//在非阻塞模式下,serverSocketChannel.accept()有可能返回null
//判断socketChannel是否为null,可以使程序更加健壮,避免NullPointerException
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (socketChannel== null)return;
System.out.println("接收到客户连接,来自:" +
socketChannel.socket().getInetAddress() +
":" + socketChannel.socket().getPort());
ChannelIO cio =new ChannelIO(socketChannel, false /*非阻塞模式*/);
RequestHandler rh = new RequestHandler(cio);
//注册读就绪事件,把RequestHandler作为附件,
//当这种事件发生时,将由RequestHandler处理该事件
socketChannel.register(key.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, rh);
}
}
在以上AcceptHandler的handle()方法中,还创建了一个ChannelIO,RequestHandler与它关联。RequestHandler会利用ChannelIO来接收和发送数据。
5.RequestHandler类
RequestHandler先通过ChannelIO来接收HTTP请求,当接收到了HTTP请求的所有数据,就对HTTP请求数据进行解析,创建相应的Request对象,然后依据客户的请求内容,创建相应的Response对象,最后发送Response对象中包含的HTTP响应数据。为了简化程序,RequestHandler仅仅支持GET和HEAD这两种请求方式。例程5是RequestHandler的源程序:
//例程5 RequestHandler.java
//此处省略import语句
public class RequestHandler implements Handler {
private ChannelIO channelIO;
private ByteBuffer requestByteBuffer = null; //存放HTTP请求的缓冲区
private boolean requestReceived = false; //表示是否已经接收到HTTP请求的所有数据
private Request request = null; //表示HTTP请求
private Response response = null; //表示HTTP响应
RequestHandler(ChannelIO channelIO) {
this.channelIO = channelIO;
}
/* 接收HTTP请求,如果已经接收到了HTTP请求的所有数据,就返回true,否则返回false */
private boolean receive(SelectionKey sk) throws IOException {
ByteBuffer tmp = null;
if (requestReceived)return true; //如果已经接收到HTTP请求的所有数据,就返回true
//如果已经读到通道的末尾,或者已经读到HTTP请求数据的末尾标志,就返回true
if ((channelIO.read() < 0) || Request.isComplete(channelIO.getReadBuf())) {
requestByteBuffer = channelIO.getReadBuf();
return (requestReceived = true);
}
return false;
}
/*
* 通过Request类的parse()方法,解析requestByteBuffer中的HTTP请求数据,
* 构造相应的Request对象
*/
private boolean parse() throws IOException {
try {
request = Request.parse(requestByteBuffer);
return true;
} catch (MalformedRequestException x) {
//如果HTTP请求的格式不正确,就发送错误信息
response = new Response(Response.Code.BAD_REQUEST,
new StringContent(x));
}
return false;
}
/* 创建HTTP响应 */
private void build() throws IOException {
Request.Action action = request.action();
//仅仅支持GET和HEAD请求方式
if ((action != Request.Action.GET) &&
(action != Request.Action.HEAD)){
response = new Response(Response.Code.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED,
new StringContent("Method Not Allowed"));
}else{
response = new Response(Response.Code.OK,
new FileContent(request.uri()), action);
}
}
/* 接收HTTP请求,发送HTTP响应 */
public void handle(SelectionKey sk) throws IOException {
try {
if (request == null) { //如果还没有接收到HTTP请求的所有数据
//接收HTTP请求
if (!receive(sk))return;
requestByteBuffer.flip();
//如果成功解析了HTTP请求,就创建一个Response对象
if (parse())build();
try {
response.prepare(); //准备HTTP响应的内容
} catch (IOException x) {
response.release();
response = new Response(Response.Code.NOT_FOUND,
new StringContent(x));
response.prepare();
}
if (send()) {
//如果HTTP响应没有发送完毕,则需要注册写就绪事件,
//以便在写就绪事件发生时继续发送数据
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
} else {
//如果HTTP响应发送完毕,就断开底层的连结,
//并且释放Response占用的资源
channelIO.close();
response.release();
}
} else { //如果已经接收到HTTP请求的所有数据
if (!send()) { //如果HTTP响应发送完毕
channelIO.close();
response.release();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
channelIO.close();
if (response != null) {
response.release();
}
}
}
/* 发送HTTP响应,如果全部发送完毕,就返回false,否则返回true */
private boolean send() throws IOException {
return response.send(channelIO);
}
}
|