|
receive()方法的许多代码都涉及对ByteBuffer的三个属性(position、limit和capacity)的操作,图4演示了以上readBuff和buffer变量的三个属性的变化过程。假定SocketChannel的read()方法读入了6个字节,把它存放在readBuff中,并假定buffer中原来有10个字节,buffer.put(readBuff)方法把readBuff中的6个字节拷贝到buffer中,buffer中最后有16个字节。
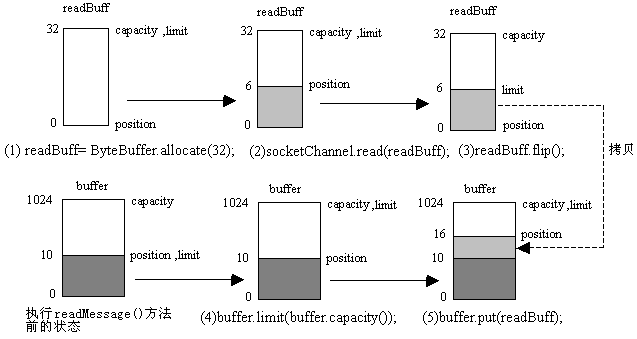
图4 receive()方法操纵readBuff和buffer的过程
如果SelectionKey的isWritable()方法返回true,就意味着这个SelectionKey所感兴趣的写就绪事件已经发生了。EchoServer类的send()方法负责处理这一事件:
public void send(SelectionKey key)throws IOException{
//获得与SelectionKey关联的ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer=(ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
//获得与SelectionKey关联的SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel=(SocketChannel)key.channel();
buffer.flip(); //把极限设为位置,把位置设为0
//按照GBK编码,把buffer中的字节转换为字符串
String data=decode(buffer);
//如果还没有读到一行数据,就返回
if(data.indexOf("\r\n")==-1)return;
//截取一行数据
String outputData=data.substring(0,data.indexOf("\n")+1);
System.out.print(outputData);
//把输出的字符串按照GBK编码,转换为字节,把它放在outputBuffer中
ByteBuffer outputBuffer=encode("echo:"+outputData);
//输出outputBuffer中的所有字节
while(outputBuffer.hasRemaining())
socketChannel.write(outputBuffer);
//把outputData字符串按照GBK编码,转换为字节,把它放在ByteBuffer中
ByteBuffer temp=encode(outputData);
//把buffer的位置设为temp的极限
buffer.position(temp.limit());
//删除buffer中已经处理的数据
buffer.compact();
//如果已经输出了字符串“bye\r\n”,就使SelectionKey失效,并关闭SocketChannel
if(outputData.equals("bye\r\n")){
key.cancel();
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("关闭与客户的连接");
}
}
EchoServer的receive()方法把读入的数据都放到一个ByteBuffer中,send()方法就从这个ByteBuffer中取出数据。如果ByteBuffer中还没有一行字符串,就什么也不做,直接退出send()方法;否则,就从ByteBuffer中取出一行字符串XXX,然后向客户发送echo:XXX。接着,send()方法把ByteBuffer中的字符串XXX删除。如果send()方法处理的字符串为“bye\r\n”,就使SelectionKey失效,并关闭SocketChannel,从而断开与客户的连接。
在ByteBuffer中存放的是字节,它表示字符串的编码。而程序需要把字节转换为字符串,才能进行字符串操作,比如判断里面是否包含“\r\n”,以及截取子字符串。EchoServer类的实用方法decode()负责解码,也就是把字节序列转换为字符串:
public String decode(ByteBuffer buffer){ //解码
CharBuffer charBuffer= charset.decode(buffer);
return charBuffer.toString();
}
decode()方法中的charset变量是EchoServer类的成员变量,它表示GBK中文编码,它的定义如下:
private Charset charset=Charset.forName("GBK");
在send()方法中,当通过SocketChannel的write(ByteBuffer buffer)方法发送数据时,write(ByteBuffer buffer)方法不能直接发送字符串,而只能发送ByteBuffer中的字节。因此程序需要对字符串进行编码,把它们转换为字节序列,放在ByteBuffer中,然后再发送。
ByteBuffer outputBuffer=encode("echo:"+outputData);
while(outputBuffer.hasRemaining())
socketChannel.write(outputBuffer);
EchoServer类的实用方法encode()负责编码,也就是把字符串转换为字节序列:
public ByteBuffer encode(String str){ //编码
return charset.encode(str);
}
在send()方法的outputBuffer中存放了字符串echo:XXX的编码。在非阻塞模式下,SocketChannel.write(outputBuffer)方法并不保证一次就把outputBuffer中的所有字节发送完,而是奉行能发送多少就发送多少的原则。如果希望把outputBuffer中的所有字节发送完,需要采用以下循环:
while(outputBuffer.hasRemaining()) //hasRemaining()方法判断是否还有未处理的字节
socketChannel.write(outputBuffer);
与SelectionKey关联的ByteBuffer附件中存放了读操作与写操作的共享数据。receive()方法把读到的数据放入ByteBuffer,而send()方法从ByteBuffer中一行行地取出数据。当send()方法从ByteBuffer中取出一行字符串XXX,就要把字符串从ByteBuffer中删除。在send()方法中,outputData变量就表示取出的一行字符串XXX,程序先把它编码为字节序列,放在一个名为temp的ByteBuffer中。接着把buffer的位置设为temp的极限,然后调用buffer的compact()方法删除代表字符串XXX的数据。
ByteBuffer temp=encode(outputData);
buffer.position(temp.limit());
buffer.compact();
图5演示了以上代码操纵buffer的过程。图5中假定temp中有10个字节,buffer中本来有16个字节,buffer.compact()方法删除缓冲区开头的10个字节,最后剩下6个字节。
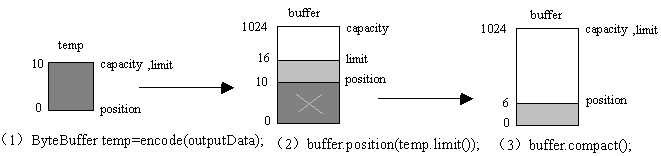
图5 从buffer中删除已经处理过的一行字符串XXX
下例程1是EchoServer的源程序。
//例程1 EchoServer.java(非阻塞模式)
package nonblock;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
public class EchoServer{
private Selector selector = null;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
private int port = 8000;
private Charset charset=Charset.forName("GBK");
public EchoServer()throws IOException{
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel= ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().setReuseAddress(true);
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
System.out.println("服务器启动");
}
public void service() throws IOException{
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT );
while (selector.select() > 0 ){
Set readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = readyKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key=null;
try{
key = (SelectionKey) it.next();
it.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) ssc.accept();
System.out.println("接收到客户连接,来自:" +
socketChannel.socket().getInetAddress() +
":" + socketChannel.socket().getPort());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
socketChannel.register(selector,
SelectionKey.OP_READ |
SelectionKey.OP_WRITE, buffer);
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
receive(key);
}
if (key.isWritable()) {
send(key);
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
try{
if(key!=null){
key.cancel();
key.channel().close();
}
}catch(Exception ex){e.printStackTrace();}
}
}//#while
}//#while
}
public void send(SelectionKey key)throws IOException{
ByteBuffer buffer=(ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
SocketChannel socketChannel=(SocketChannel)key.channel();
buffer.flip(); //把极限设为位置,把位置设为0
String data=decode(buffer);
if(data.indexOf("\r\n")==-1)return;
String outputData=data.substring(0,data.indexOf("\n")+1);
System.out.print(outputData);
ByteBuffer outputBuffer=encode("echo:"+outputData);
while(outputBuffer.hasRemaining()) //发送一行字符串
socketChannel.write(outputBuffer);
ByteBuffer temp=encode(outputData);
buffer.position(temp.limit());
buffer.compact(); //删除已经处理的字符串
if(outputData.equals("bye\r\n")){
key.cancel();
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("关闭与客户的连接");
}
}
public void receive(SelectionKey key)throws IOException{
ByteBuffer buffer=(ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
SocketChannel socketChannel=(SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuff= ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
socketChannel.read(readBuff);
readBuff.flip();
buffer.limit(buffer.capacity());
buffer.put(readBuff); //把读到的数据放到buffer中
}
public String decode(ByteBuffer buffer){ //解码
CharBuffer charBuffer= charset.decode(buffer);
return charBuffer.toString();
}
public ByteBuffer encode(String str){ //编码
return charset.encode(str);
}
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
EchoServer server = new EchoServer();
server.service();
}
}
2.在EchoServer中混合用阻塞模式与非阻塞模式
在例程1中,EchoServer的ServerSocketChannel以及SocketChannel都被设置为非阻塞模式,这使得接收连接、接收数据和发送数据的操作都采用非阻塞模式,EchoServer采用一个线程同时完成这些操作。假如有许多客户请求连接,可以把接收客户连接的操作单独由一个线程完成,把接收数据和发送数据的操作由另一个线程完成,这可以提高服务器的并发性能。
负责接收客户连接的线程按照阻塞模式工作,如果收到客户连接,就向Selector注册读就绪和写就绪事件,否则进入阻塞状态,直到接收到了客户的连接。负责接收数据和发送数据的线程按照非阻塞模式工作,只有在读就绪或写就绪事件发生时,才执行相应的接收数据和发送数据操作。
例程2是EchoServer类的源程序。其中receive()、send()、decode()和encode()方法的代码与例程1的EchoServer类相同,为了节省篇幅,不再重复显示。
//例程2 EchoServer.java(混合使用阻塞模式与非阻塞模式)
package thread2;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
public class EchoServer{
private Selector selector = null;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
private int port = 8000;
private Charset charset=Charset.forName("GBK");
public EchoServer()throws IOException{
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel= ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().setReuseAddress(true);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
System.out.println("服务器启动");
}
public void accept(){
for(;;){
try{
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("接收到客户连接,来自:" +
socketChannel.socket().getInetAddress() +
":" + socketChannel.socket().getPort());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
synchronized(gate){
selector.wakeup();
socketChannel.register(selector,
SelectionKey.OP_READ |
SelectionKey.OP_WRITE, buffer);
}
}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
}
private Object gate=new Object();
public void service() throws IOException{
for(;;){
synchronized(gate){}
int n = selector.select();
if(n==0)continue;
Set readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = readyKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key=null;
try{
key = (SelectionKey) it.next();
it.remove();
if (key.isReadable()) {
receive(key);
}
if (key.isWritable()) {
send(key);
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
try{
if(key!=null){
key.cancel();
key.channel().close();
}
}catch(Exception ex){e.printStackTrace();}
}
}//#while
}//#while
}
public void send(SelectionKey key)throws IOException{…}
public void receive(SelectionKey key)throws IOException{… }
|